LED Blink Tutorial with Arduino and Rhinobot
Introduction
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are simple yet essential electronic components used in various applications, from indicators to displays. In this tutorial, we will learn about LEDs, how to connect them to an Arduino Uno, their placement on the Rhinobot controller board, and how to program them to blink using Arduino.
Understanding LED and Its Pins
An LED consists of two terminals:
- Anode (+): The longer leg, which should be connected to a positive voltage.
- Cathode (-): The shorter leg, which should be connected to the ground (GND).

Connecting LED to Arduino Nano
To connect an LED to an Arduino Nano, follow these steps:
- Connect the anode (longer leg) of the LED to digital pin 3 on the Arduino through a 220Ω resistor.
- Connect the cathode (shorter leg) of the LED to the GND pin of the Arduino.
- Ensure the connections are secure before powering on the Arduino.

Locating the LED on the Rhinobot Controller Board
The Rhinobot controller board makes it easier to learn LED controls. All the connections have already been done on the board, and all you have to do is learn how to code, making it relatively easier for beginners.
The LED is connected to pin 3 on the controller board, and we can complete the circuit by connecting a jumper cap to the LED pins.

Arduino Code to Turn On LED
void setup() {
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
}
- void setup() – The code written inside this function will run only once.
- pinMode(3, OUTPUT) – sets digital pin 3 as an OUTPUT to send signals (e.g., turn on an LED).
- digitalWrite(3, HIGH) – sets digital pin 3 to HIGH, turning it ON (5V) to power a connected device like an LED.
Arduino Code for LED Blinking
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(3, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
- void loop() – The code written inside this function will be executed repeatedly.
- digitalWrite(3, HIGH) – This turns on the LED.
- delay(1000) – This line pauses the code execution for 1000 milliseconds or 1 second.
- digitalWrite(3, LOW) – This turns off the LED.
- delay(1000) – This line again pauses the code execution for 1 second.
Uploading the Code to Arduino
- Open the Arduino IDE:
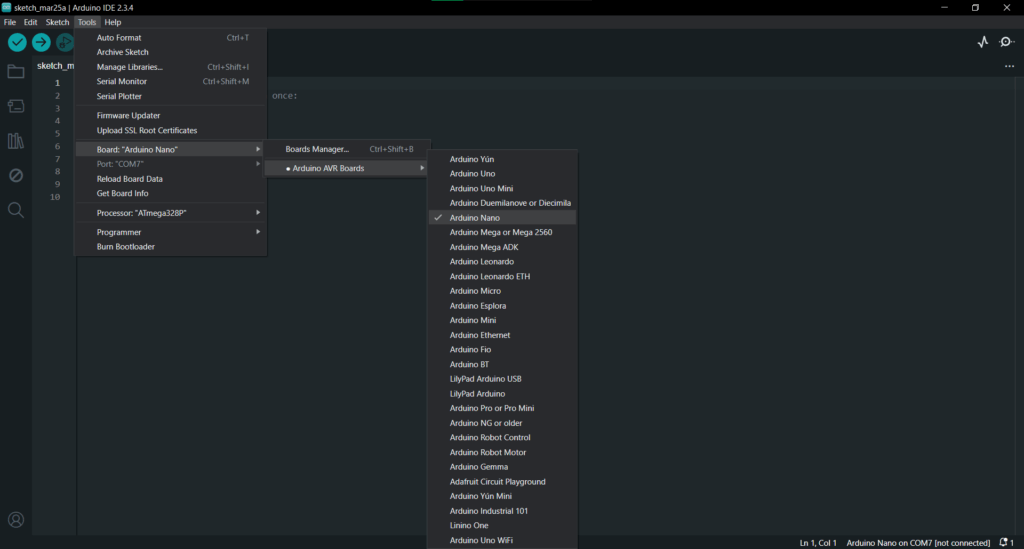
- Connect your Arduino Nano to your computer via USB.Select the correct board: Tools > Board > Arduino Nano.
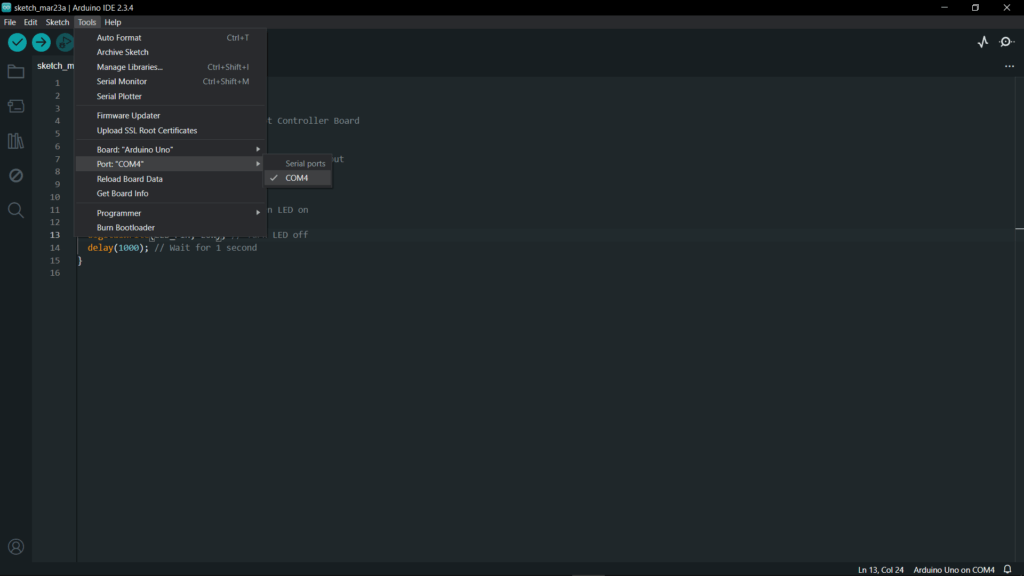
- Select the correct port: Tools > Port > (your Arduino port).
- Copy and paste the above code into the Arduino IDE.

- Click on the Upload button or alternatively press Ctrl + U.

- Once uploaded, the LED should start blinking every second.

Conclusion
Blinking an LED is the first step in learning Arduino programming. Understanding pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and delay() functions helps build the foundation for more complex projects. You can now try modifying the blink interval or controlling multiple LEDs for advanced experimentation.
